Cybercrime may not be the first thing that comes to mind when you think of Canada, but these days cybercrime is top of mind for many Canadian small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). In a recent survey of more than 1,000 people working in IT at Canadian companies with less than 500 employees, almost two-thirds (64%) said IT security and protection of business data was very important. Only two other activities were seen as more important: improving quality of products and services (68%), and growing client base and revenues (65%).
And Canadian SMBs have good reason to be concerned. The survey, conducted by Ipsos and sponsored by ESET, found that one in four Canadian SMBs with yearly revenues of $10 million or more had been hit by a cyberattack. As my colleague, Iva Peric-Lightfoot, manager of ESET Canada, put it, these SMBs have many of the same digital assets that criminals target in enterprise-level organizations, “but tend to have a lower level of protection and less sophisticated security solutions in place”.
I have previously referred to this phenomenon as the SMB cybercrime sweet spot. Relative to consumers, SMBs have more digital assets and cash that is worth targeting via criminal hacking. Relative to enterprises, SMBs have fewer cybersecurity protections in place. You can see this visualized in the accompanying graphic:
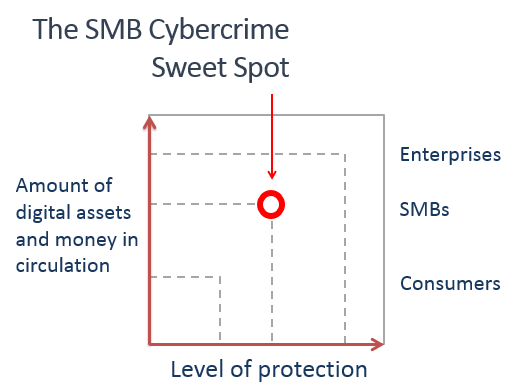
This latest survey tends to validate the SMB sweet spot concept. It shows cyberattack risk spiking for Canadian SMBs once they reach $10 million in annual revenue, with one in four becoming victims, compared to only one in 10 firms with annual revenue under $10 million. Not that the latter have nothing to worrying about, far from it. For a start, many small firms are working hard to grow their revenues, but they might not be fully aware of the cybercrime risks inherent in such growth.
Making adequate financial provisions for dealing with increased cyber risks as your business grows is clearly a prudent strategy and one that I would strongly recommend. However, it is not clear if Canadian SMBs are getting this message. For example, the survey revealed a disconnect among employees regarding, on the one hand, their company’s allocation of resources to cybersecurity, and on the other, confidence regarding their company’s level of protection from attack. While seven in 10 Canadians employed at SMBs feel their company is devoting enough resources to the issue, only one-third feel ‘very confident’ their company is safe from a cyberattack.
We sometimes see this type of disconnect when people are not fully aware of the threats that their organizations face from cybercriminals. For example, any organization that is serious about cybersecurity will perform a risk analysis to determine what digital assets are at risk and what level that risk is at. If a firm is not aware that criminals can sell its customer data for good prices on black markets will little chance of arrest, or make money by renting out its hijacked servers for use in malicious activities, then that company is probably under-estimating its cyber risks.
Unfortunately, the survey revealed that less than one-third of Canadian SMBs are ‘very familiar’ with the concepts of ransomware, social engineering, and two-factor authentication, yet these are hot topics in cybersecurity right now. The implications are serious here because SMBs make up most of Canada’s economy, but the survey findings indicate that many of them would be unable to function for more than a few days without access to their data. Specifically, 65% of Canadian SMBs said they could only function for a few hours or days without access to their data, and a full 15% said they would have to cease functioning immediately.
The picture of Canadian SMB cybersecurity that emerges from this survey is of many good intentions and a broad awareness that cybercrime is a threat to organizations. For instance, 96% of SMB employees think backing up company files is important, and 92% think having IT security software installed on all devices is an important IT security measure. A very encouraging 88% place a strong emphasis on “training on your company’s IT security procedures”. Yet much work remains to be done. Only 43% on SMB employees felt confident that their business and its reputation could “survive and thrive” after a cyberattack. And only 40% said they were “very satisfied” with their company’s current IT security policies, procedures, and products.
With clear evidence that the risk of cyberattack increases with revenue growth there is a definite need for Canadian SMBs to keep improving their awareness of threats and their ability to deflect them. And there is plenty of room to better align cyber policy, procedure, and product selection with the full range threats, because the threats are unlikely to diminish any time soon.




